The Next generation of ECO SHIP
The Next generation of ECO SHIPThe Electric propulsion ship "SENSHO" Development
The development of electric ship propulsion to date has seen the technology used in various types of vessel. Research ships (where a reduction in engine vibration is desirable), high-class passenger cruise ships and icebreakers (whose load fluctuation when operating in icepacks can vary greatly).
During the 1990's great technical progress was made in the development of electric propulsion. The ship SENSHO utilizes this technology and becomes part of the new generation of ECO SHIPS.
"A ship that makes you excited"
The SENSHO was developed in collaboration with a variety of specialists.
A large electrical manufacturer, a fluid laboratory, a transportation facilities repair group and a research team based at Hiroshima University.
The current shipbuilding climate is one of ever increasing globalization.
There are two directions in which the shipping industry is heading today with ever-greater specialization.
Standard Ships: These vessels are constructed with the cooperation of China and SE Asia and are cheap but less advanced.
State of the Art Vessels:Designed and constructed in Japan, they utilize the latest technology that is only available in the most experienced shipbuilding yards.
Research background
PODD type promotion devices were developed in Europe. Subsequent Synthesis improved these devices by 8-15%, as was proven by our miniature model bench tests.
SENSHO research outline
| A present chemical tanker | SENSHO Development | ||
| Aggregate tonnage | 499 tons | Aggregate tonnage | 499 tons |
| Entire length | 66. 5m(218. 17ft) | Entire length | 66. 5m(218. 17ft) |
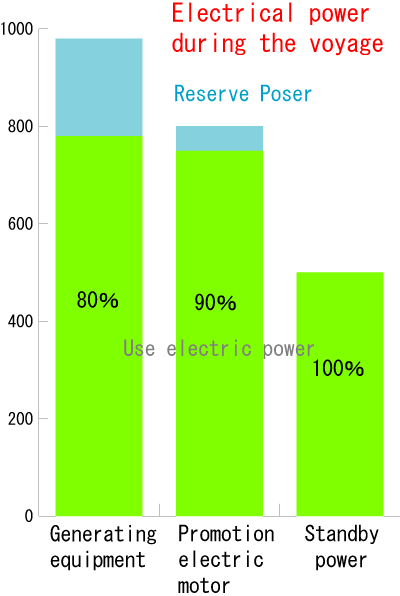
| Promotion electric motor | 365kw*2set | Promotion electric motor | 365kw*2set |
| Full load speed | 11. 6knot | Full load speed | 11. 6knot |
| Promotion vessel | A variable pace | Promotion vessel | hard vertical type 4 wing variable 2 base |
| Freight pump | 6 base | Freight pump | 6 units(It is installed in the stand-alone version and each tank. ) |
A water tank examination by the model is enforced
Stern Ship Type: The adoption of Buttock flow ship types. The flow of water around the hull exfoliates. Exfoliation occurs across the entire cross direction of the ship. Consequently, we were able to investigate the limit of buttock inclination.
A center skeg is necessary from the point of view of navigational performance. The optimum size of the center skeg and its resultant influence of flow were investigated. The improvement of flow, which was obtained through the development of the skeg, profits the propeller.
Expected effect
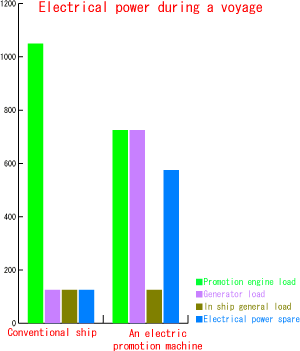
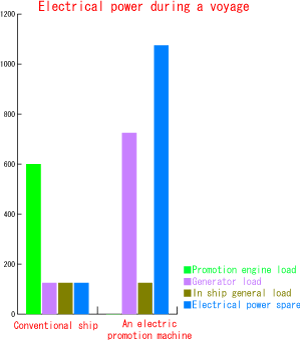
As the hull form has been simplified, building costs have been reduced by 10% and propulsive efficiency has risen 20%. (This represents a decrease in fuel consumption of: 254 kl/year age which equates to 7,620,000yen a year assuming a unit fuel cost of 30,000yen).
The fattening of the stern has reduced hull vibration and the decreased width of the bow has lowered the wave resistance.
CO2 and NOx emissions were reduced by 20 and 40% respectively.
The safety of the ship is ensured by multiple redundancy; two main machines, two shafts, two sheet rudders and bow and stern thrusters.
Stop Free Maintenance (Main machinery can be maintained even when not at anchor).
Even if a promotion system breaks down, nine knots can be maintained.